Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
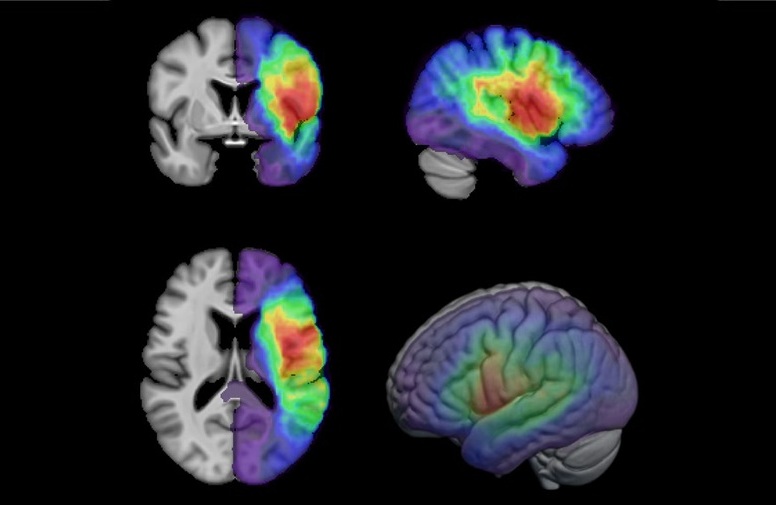
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
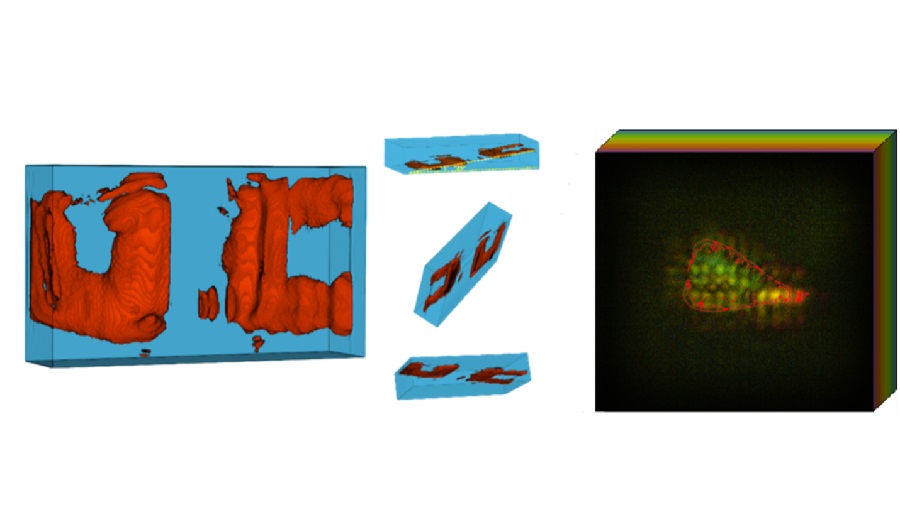
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
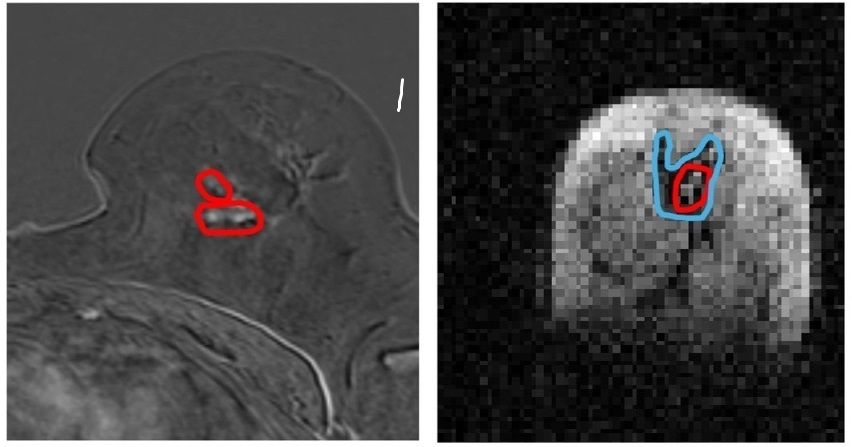
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
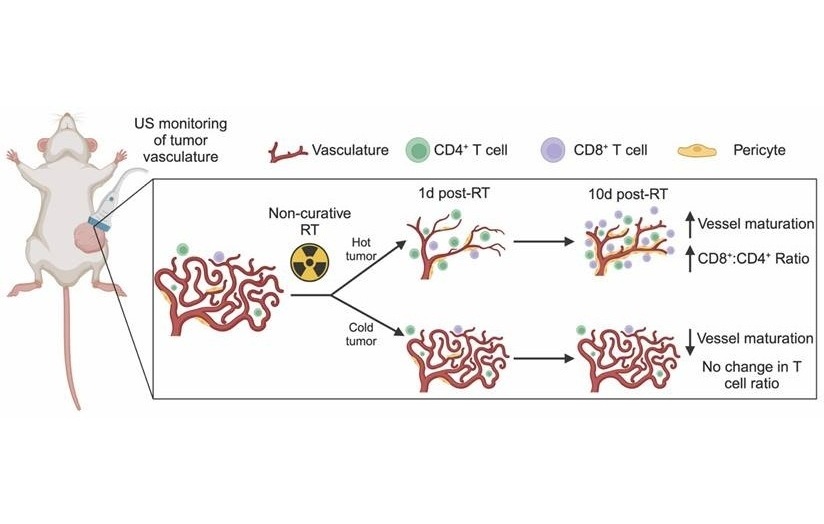
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
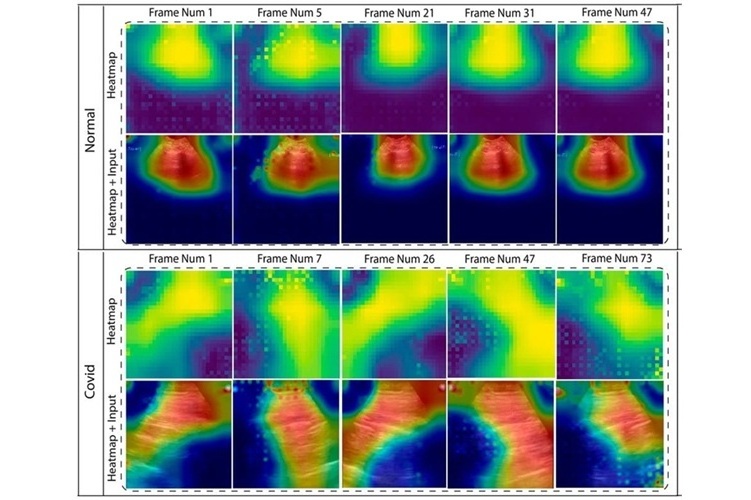
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology



















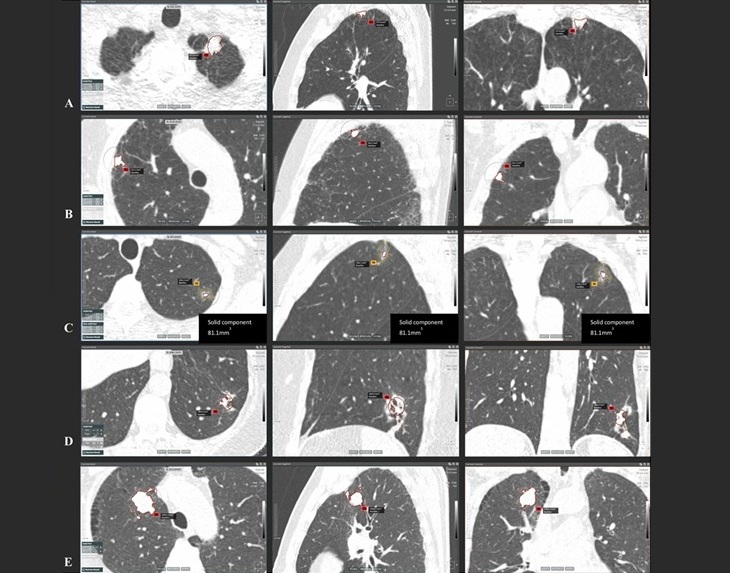
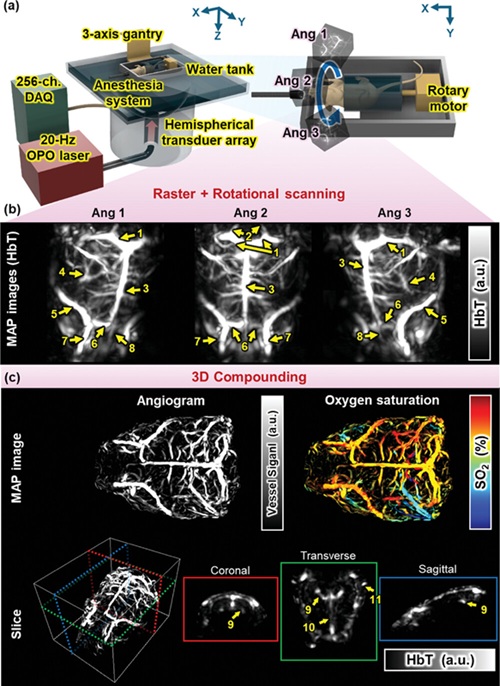
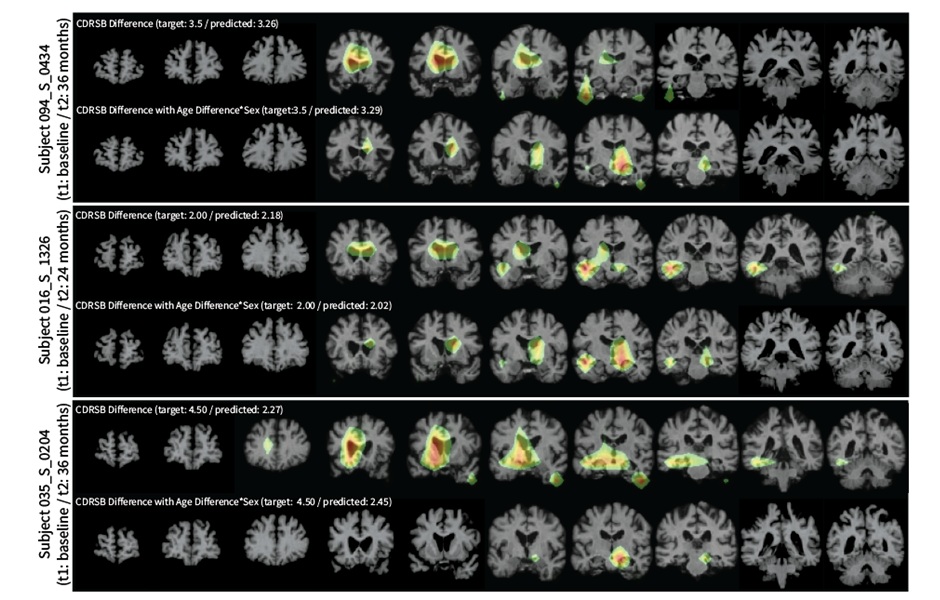




.jpg)
.jpeg)



