Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- Injury Prediction Rule Reduces Radiographic Imaging Exposure in Children
- AI Detects More Breast Cancers with Fewer False Positives
- AI-Powered Portable Thermal Imaging Solution Could Complement Mammography for Breast Cancer Screening
- Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- World’s First Reference Material to Improve Accuracy of MRI and CT Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
- New MRI Method “Lights Up” Pancreatic Cancer
- Biology-Driven Radiomics Approach to Identify Rectal Cancer Patients without Tumor Post Therapy
- New Eye Tracking Controlled VR System Enhances MRI Scans for Young Children
- AI Outperforms Radiologists in Detecting Prostate Cancer on MRI
- New Imaging Technique Detects Aggressive Lung and Prostate Cancers
- First Specific PET Scan for TB to Improve Treatment
- PET/CT Superior at Lesion Detection for Head and Neck Paragangliomas than Gold Standard MRI
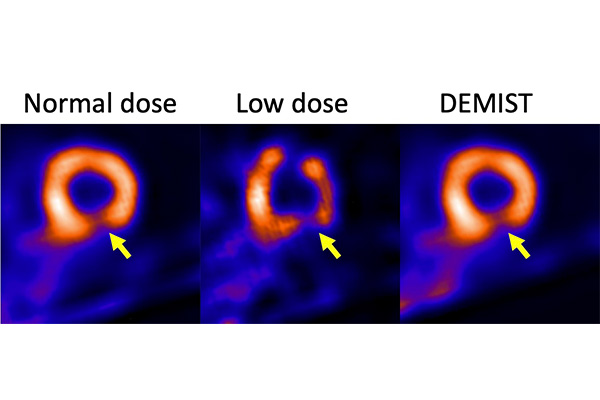
- New Radiotracer Generates High Quality and Readily Interpretable Images of Cardiac Amyloidosis
- New PET Radiotracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Key Gastrointestinal Cancer Biomarker
- Ultrasound Beam Triggers ‘Nanodroplets' For Targeted Drug Delivery
- Ultrasound Technology Breaks Blood-Brain Barrier for Glioblastoma Treatment
- Implantable Ultrasound Device Could Replace Electrodes for Deep Brain Stimulation
- Robotic Ultrasound Systems to Assist Doctors during Surgery
- Functional Ultrasound Imaging Records Brain Activity through Transparent Skull Implant
- Artificial Intelligence Tool Enhances Usability of Medical Images
- New AI Tool Accurately Detects Six Different Cancer Types on Whole-Body PET/CT Scans
- Innovative Imaging Technique Helps Assess Bone Loss after Bariatric Surgery
- Imaging Software Improves Lung Diagnosis in Patients Allergic To Medical Contrast Dye
- Bone Density Test Uses Existing CT Images to Predict Fractures
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
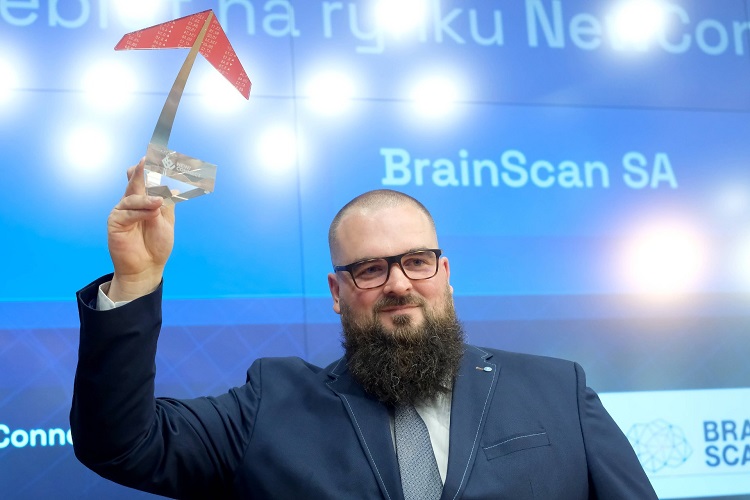
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
- Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasound
General/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- Injury Prediction Rule Reduces Radiographic Imaging Exposure in Children
- AI Detects More Breast Cancers with Fewer False Positives
- AI-Powered Portable Thermal Imaging Solution Could Complement Mammography for Breast Cancer Screening
- Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- World’s First Reference Material to Improve Accuracy of MRI and CT Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
- New MRI Method “Lights Up” Pancreatic Cancer
- Biology-Driven Radiomics Approach to Identify Rectal Cancer Patients without Tumor Post Therapy
- New Eye Tracking Controlled VR System Enhances MRI Scans for Young Children
- AI Outperforms Radiologists in Detecting Prostate Cancer on MRI
- New Imaging Technique Detects Aggressive Lung and Prostate Cancers
- First Specific PET Scan for TB to Improve Treatment
- PET/CT Superior at Lesion Detection for Head and Neck Paragangliomas than Gold Standard MRI
- New Radiotracer Generates High Quality and Readily Interpretable Images of Cardiac Amyloidosis
- New PET Radiotracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Key Gastrointestinal Cancer Biomarker
- Ultrasound Beam Triggers ‘Nanodroplets' For Targeted Drug Delivery
- Ultrasound Technology Breaks Blood-Brain Barrier for Glioblastoma Treatment
- Implantable Ultrasound Device Could Replace Electrodes for Deep Brain Stimulation
- Robotic Ultrasound Systems to Assist Doctors during Surgery
- Functional Ultrasound Imaging Records Brain Activity through Transparent Skull Implant
- Artificial Intelligence Tool Enhances Usability of Medical Images
- New AI Tool Accurately Detects Six Different Cancer Types on Whole-Body PET/CT Scans
- Innovative Imaging Technique Helps Assess Bone Loss after Bariatric Surgery
- Imaging Software Improves Lung Diagnosis in Patients Allergic To Medical Contrast Dye
- Bone Density Test Uses Existing CT Images to Predict Fractures
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
- Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering