Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events

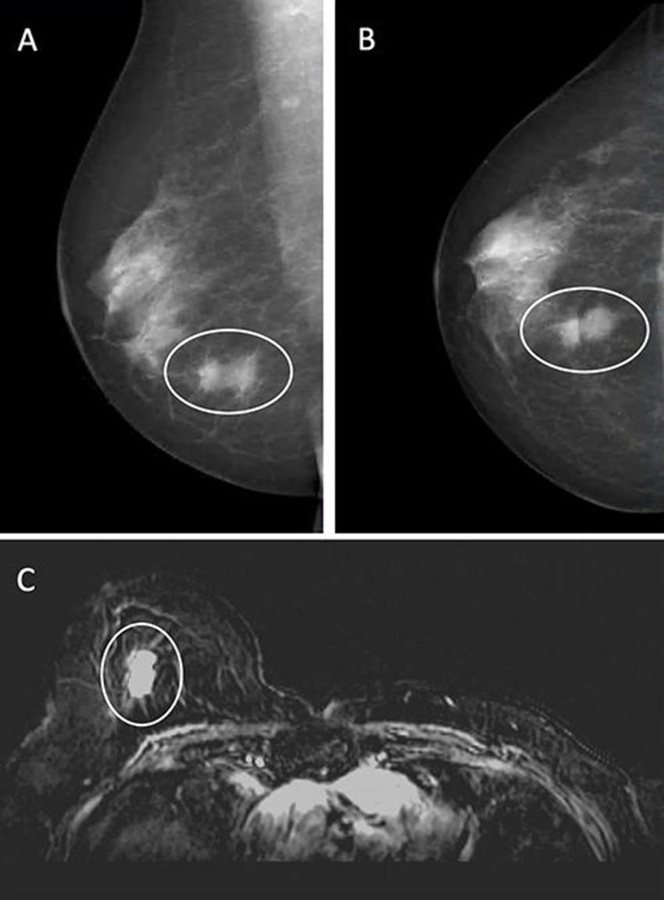
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
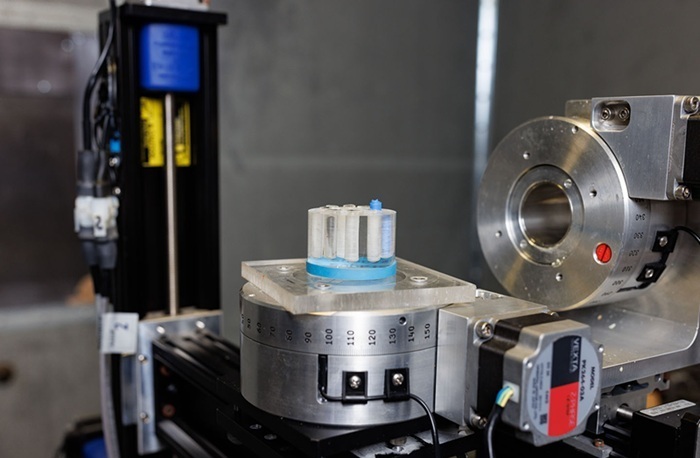
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
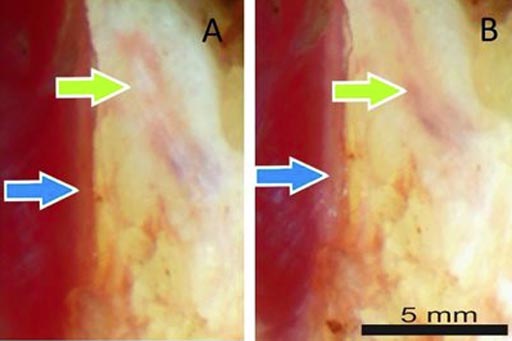
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
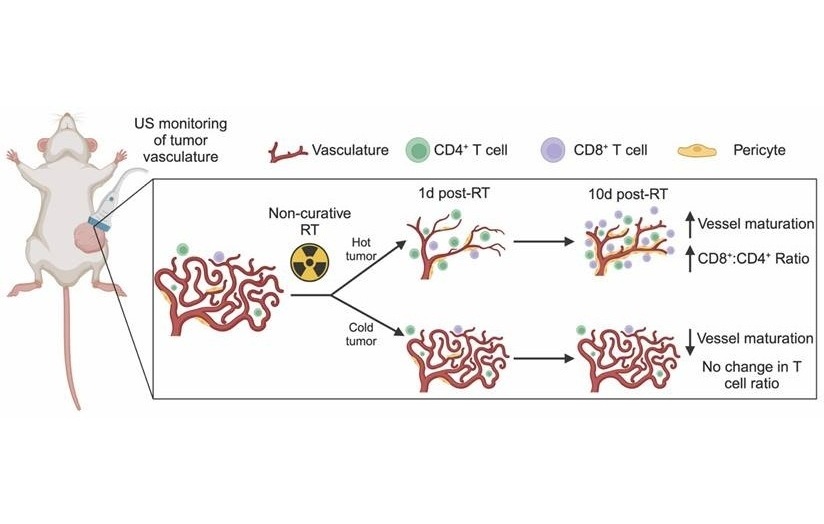
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
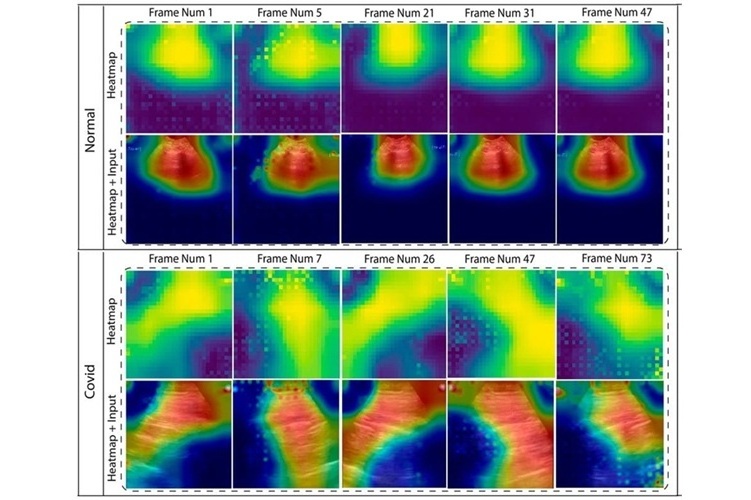
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology

















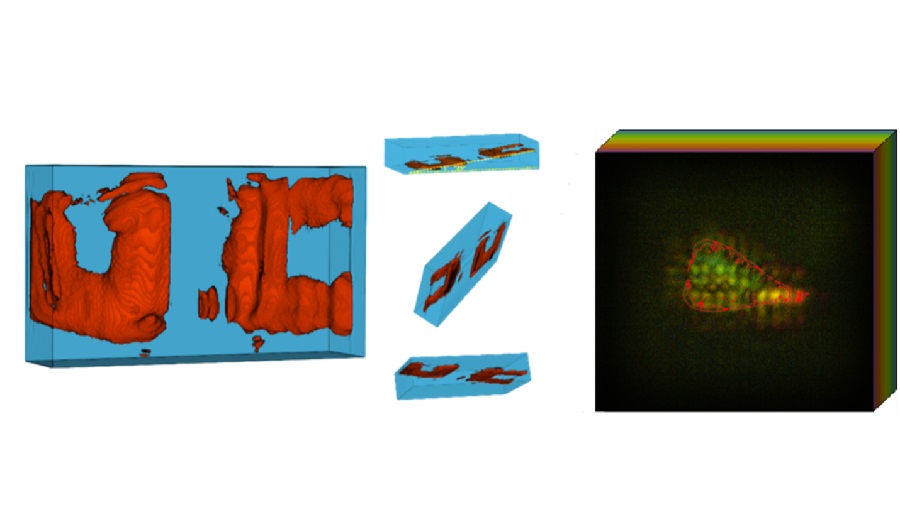



![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)
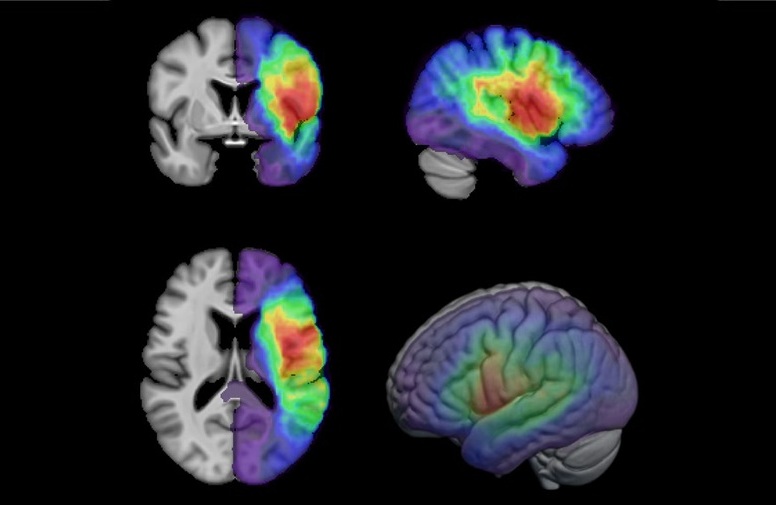
![Image: Autoradiography images showing binding of [18F]flortaucipir, [18F]MK6240, and [18F]PI2620 in prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum (A) and in whole-brain hemisphere (B) of control and AD brains (Photo courtesy of UFRGS) Image: Autoradiography images showing binding of [18F]flortaucipir, [18F]MK6240, and [18F]PI2620 in prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum (A) and in whole-brain hemisphere (B) of control and AD brains (Photo courtesy of UFRGS)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-12/F2.large.jpg)




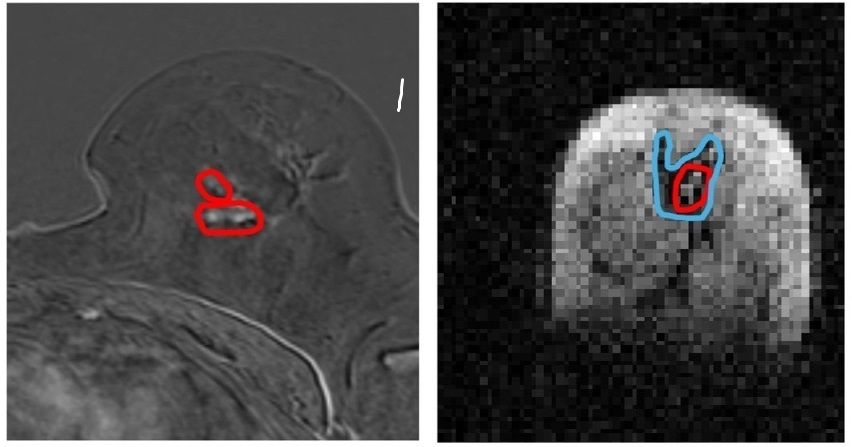
.jpg)
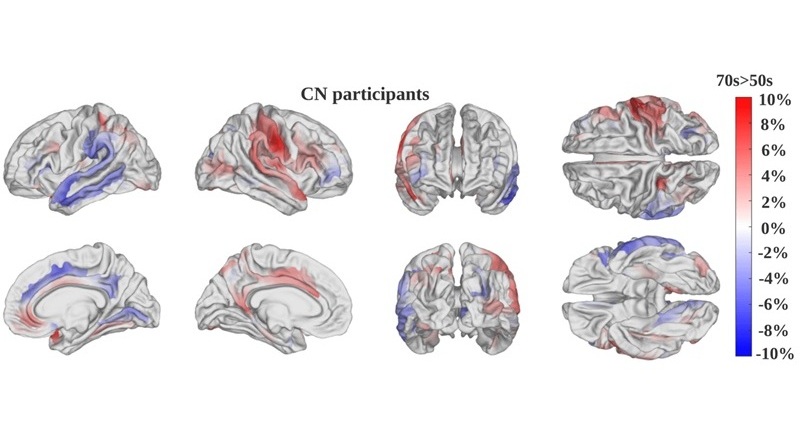
.jpeg)



