Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRI
Nuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Analysis Shows Promise in Clinical Practice
- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- Innovative X-Ray Technique Captures Human Heart with Unprecedented Detail
- Cutting-Edge Technology Enhances Chest X-Ray Classification for Superior Patient Outcomes
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Deep Learning-Based AI for Prostate MRI Helps Improve Risk Assessment and Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Breakthrough Heart MRI Technique Accurately Predicts Heart Failure Risk in General Population
- Radiology Test Non-Invasively Diagnoses Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated AKI
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- AI Powered Portable Lung Imaging Brings Life-Saving Diagnostic Capabilities to POC
- AI May Benefit Decision-Making in Less Experienced Clinicians Assessing Heart Ultrasounds
- Robotic Arm-Based Remote Echocardiograms Offer Same Diagnostic Accuracy as In-Person Echocardiography
- Ultrasound Device Noninvasively Stimulates Deep Brain Regions for Treating Chronic Pain
- New Ultrasound Terminology for Early Pregnancy Endorsed by Expert Panel
- Motion Compatible Neuroimaging Device Enables Walking PET Brain Scans
- Routine CT Screening Can Identify Individuals at Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
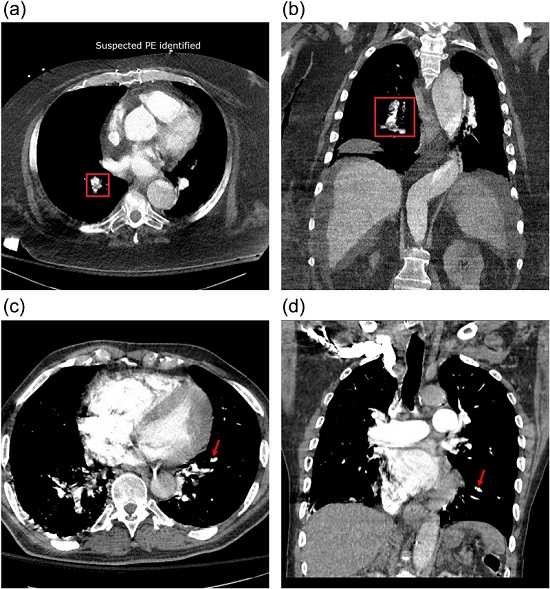
- AI-Based Algorithm Significantly Reduce Miss Rates for Pulmonary Embolism on CT Imaging
- Next Gen Interactive Plaque Analysis Platform Assesses Patient Risk in Suspected Coronary Artery Disease
- Breakthrough Brain PET System Aids Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRI
Nuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRI
Nuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Analysis Shows Promise in Clinical Practice
- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- Innovative X-Ray Technique Captures Human Heart with Unprecedented Detail
- Cutting-Edge Technology Enhances Chest X-Ray Classification for Superior Patient Outcomes
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Deep Learning-Based AI for Prostate MRI Helps Improve Risk Assessment and Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Breakthrough Heart MRI Technique Accurately Predicts Heart Failure Risk in General Population
- Radiology Test Non-Invasively Diagnoses Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated AKI
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- AI Powered Portable Lung Imaging Brings Life-Saving Diagnostic Capabilities to POC
- AI May Benefit Decision-Making in Less Experienced Clinicians Assessing Heart Ultrasounds
- Robotic Arm-Based Remote Echocardiograms Offer Same Diagnostic Accuracy as In-Person Echocardiography
- Ultrasound Device Noninvasively Stimulates Deep Brain Regions for Treating Chronic Pain
- New Ultrasound Terminology for Early Pregnancy Endorsed by Expert Panel
- Motion Compatible Neuroimaging Device Enables Walking PET Brain Scans
- Routine CT Screening Can Identify Individuals at Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- AI-Based Algorithm Significantly Reduce Miss Rates for Pulmonary Embolism on CT Imaging
- Next Gen Interactive Plaque Analysis Platform Assesses Patient Risk in Suspected Coronary Artery Disease
- Breakthrough Brain PET System Aids Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets


















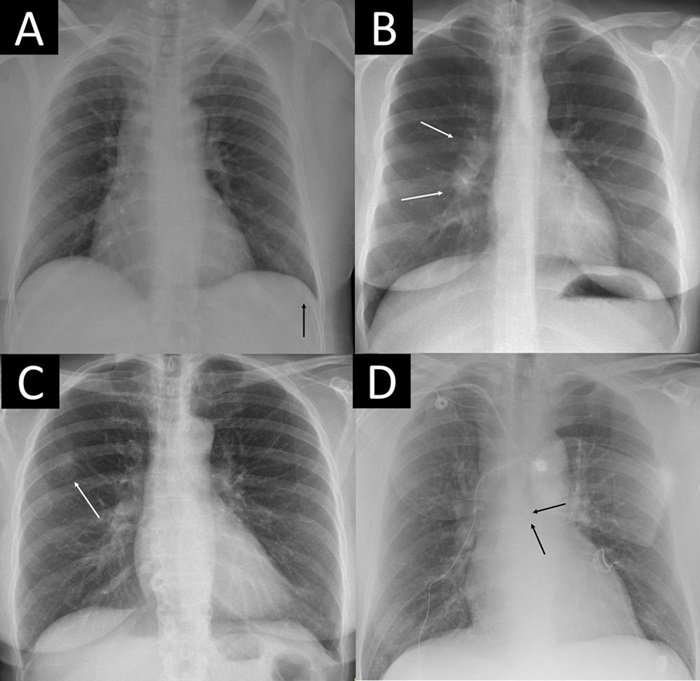
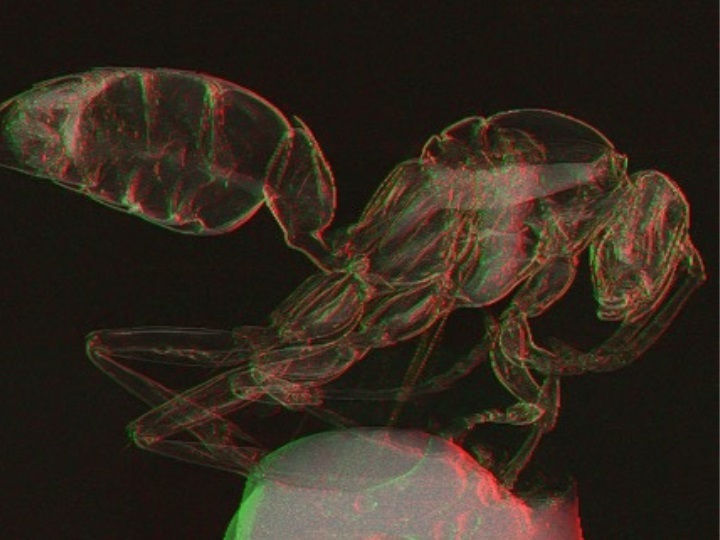


![Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine) Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-08-22/JNM Aug 2024 - Borgwardt Figure 3A.jpg)
.jpeg)