Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- Innovative X-Ray Technique Captures Human Heart with Unprecedented Detail
- Cutting-Edge Technology Enhances Chest X-Ray Classification for Superior Patient Outcomes
- AI Model Accurately Estimates Lung Function Using Chest X-Rays
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Deep Learning-Based AI for Prostate MRI Helps Improve Risk Assessment and Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Breakthrough Heart MRI Technique Accurately Predicts Heart Failure Risk in General Population
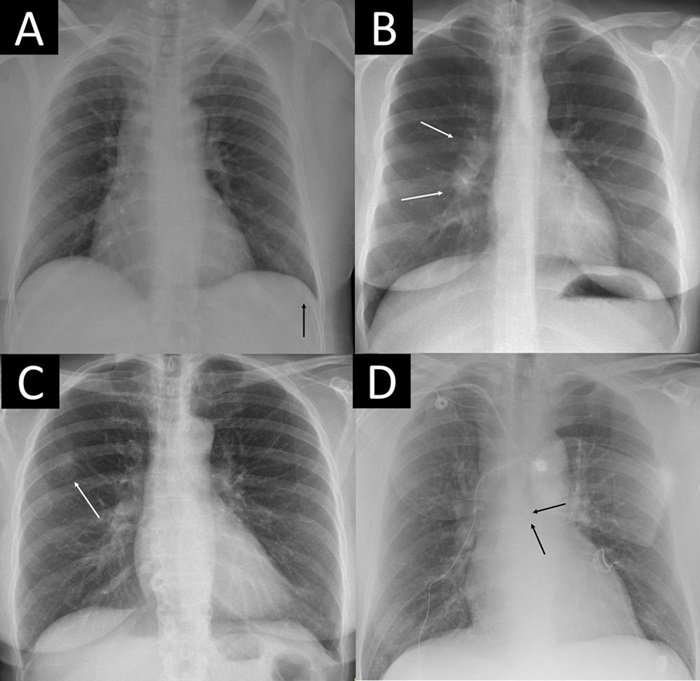
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
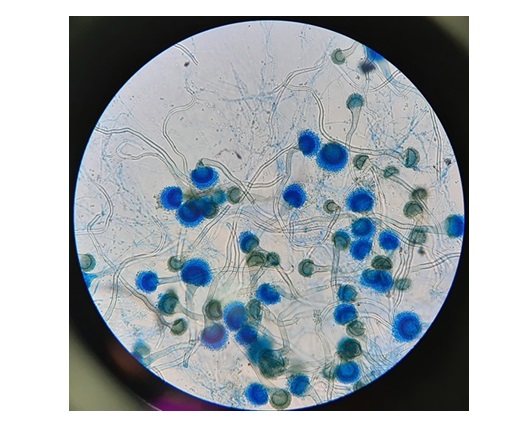
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
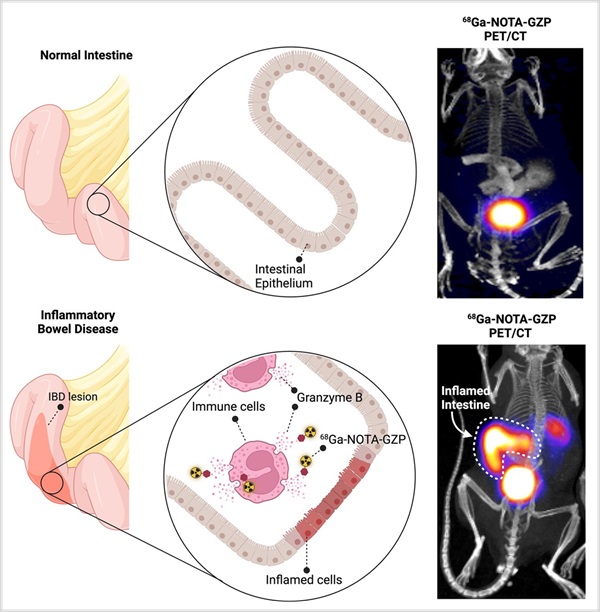
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- PET/CT Imaging Using New Tracing Agent Could Become ‘Gold Standard’ Test for Prostate Cancer Detection
- Ultrasound Device Noninvasively Stimulates Deep Brain Regions for Treating Chronic Pain
- New Ultrasound Terminology for Early Pregnancy Endorsed by Expert Panel
- AI Automates Detection of Mitral Regurgitation on Echocardiograms for Minimally Invasive Procedure
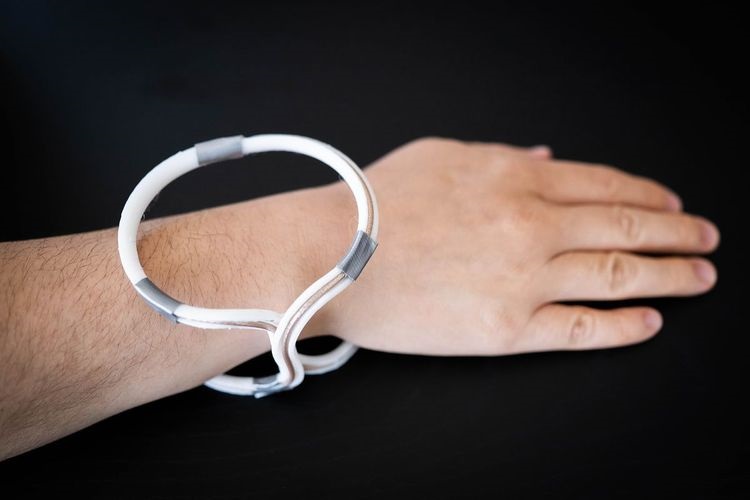
- Quantitative Ultrasound Parameters Offer New Tool for Diagnosing Lung Disease
- POC AI Tool Helps Novice Users Accurately Estimate Gestational Age from Blind Ultrasound Sweeps
- Motion Compatible Neuroimaging Device Enables Walking PET Brain Scans
- Routine CT Screening Can Identify Individuals at Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
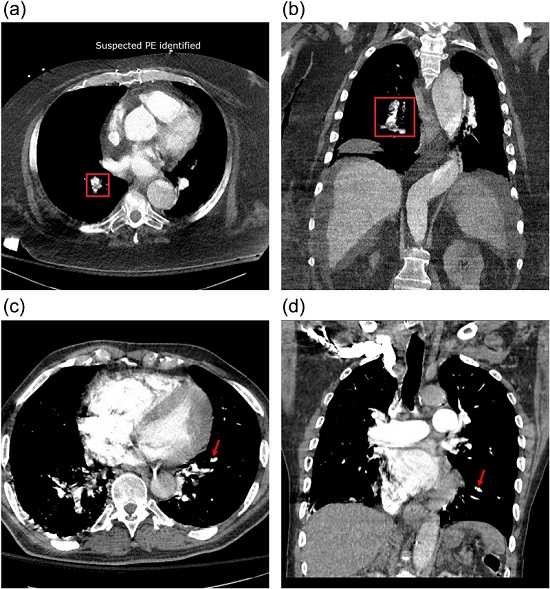
- AI-Based Algorithm Significantly Reduce Miss Rates for Pulmonary Embolism on CT Imaging
- Next Gen Interactive Plaque Analysis Platform Assesses Patient Risk in Suspected Coronary Artery Disease
- Breakthrough Brain PET System Aids Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI-Based Algorithm Improves Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnoses
- Groundbreaking X-Ray Imaging Technique Could Improve Medical Diagnostics
- Innovative X-Ray Technique Captures Human Heart with Unprecedented Detail
- Cutting-Edge Technology Enhances Chest X-Ray Classification for Superior Patient Outcomes
- AI Model Accurately Estimates Lung Function Using Chest X-Rays
- AI Software Analyzes Neuroimaging Data and Patient Information to Diagnose 10 Types of Dementia
- Metamaterials to Make MRI Scans Faster, Cheaper, and More Accurate
- Deep Learning Enables Accurate, Automated Quality Control Image Assessment for Liver MR Elastography
- Deep Learning-Based AI for Prostate MRI Helps Improve Risk Assessment and Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Breakthrough Heart MRI Technique Accurately Predicts Heart Failure Risk in General Population
- New PET/CT Technique Accurately Detects Neuroblastoma in Children with Short Scan Time and No Anesthesia
- New Imaging Method Enables Early Detection of Fungal Infections Caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus
- New Imaging Method Non-Invasively Detects Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- FAPI PET/CT Improves Staging of Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
- PET/CT Imaging Using New Tracing Agent Could Become ‘Gold Standard’ Test for Prostate Cancer Detection
- Ultrasound Device Noninvasively Stimulates Deep Brain Regions for Treating Chronic Pain
- New Ultrasound Terminology for Early Pregnancy Endorsed by Expert Panel
- AI Automates Detection of Mitral Regurgitation on Echocardiograms for Minimally Invasive Procedure
- Quantitative Ultrasound Parameters Offer New Tool for Diagnosing Lung Disease
- POC AI Tool Helps Novice Users Accurately Estimate Gestational Age from Blind Ultrasound Sweeps
- Motion Compatible Neuroimaging Device Enables Walking PET Brain Scans
- Routine CT Screening Can Identify Individuals at Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- AI-Based Algorithm Significantly Reduce Miss Rates for Pulmonary Embolism on CT Imaging
- Next Gen Interactive Plaque Analysis Platform Assesses Patient Risk in Suspected Coronary Artery Disease
- Breakthrough Brain PET System Aids Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets




















.jpg)
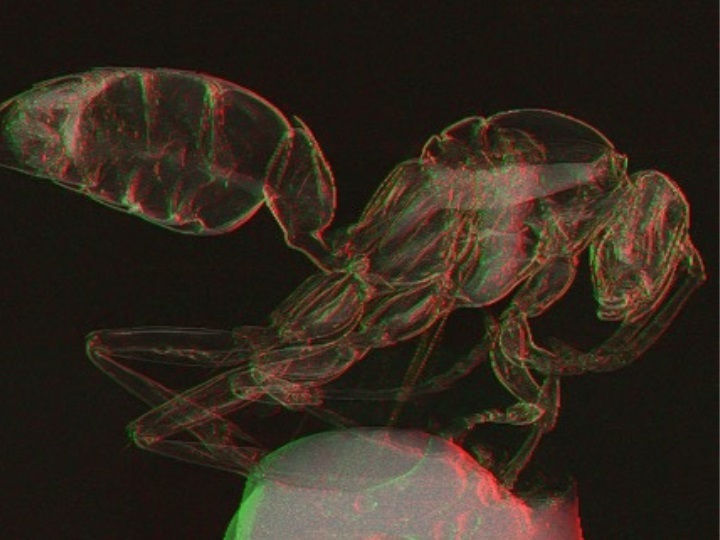
![Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine) Image: [18F]MFBG LAFOV PET/ULD CT (top) and [123I]MIBG scintigraphy with SPECT/LD CT images (bottom) of 7-wk-old girl with neuroblastoma (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-08-22/JNM Aug 2024 - Borgwardt Figure 3A.jpg)