Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events

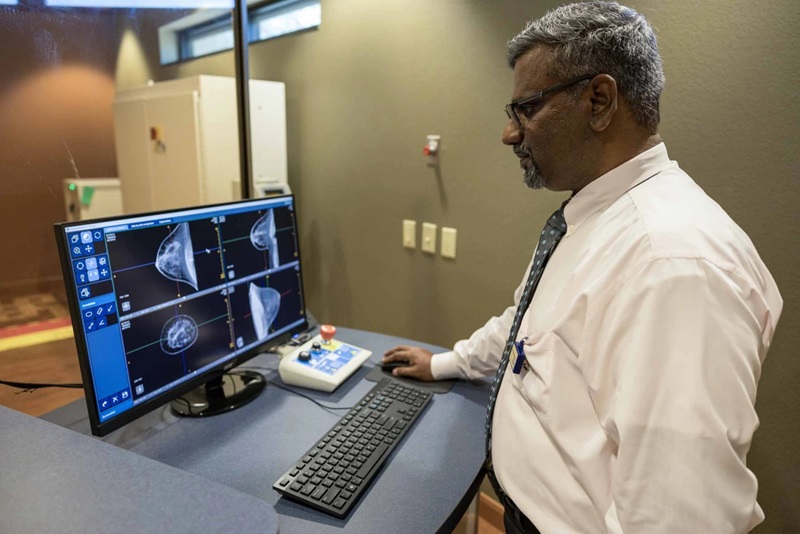
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
- AI Model Identifies Vertebral Compression Fractures in Chest Radiographs
- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
- MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy Reduces Long-Term Side Effects in Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Imaging Techniques Could Enable Surgical Removal of Prostate Cancer Without Biopsy
- AI Supported Detection of Cerebral Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Cuts Radiologic Reporting Times
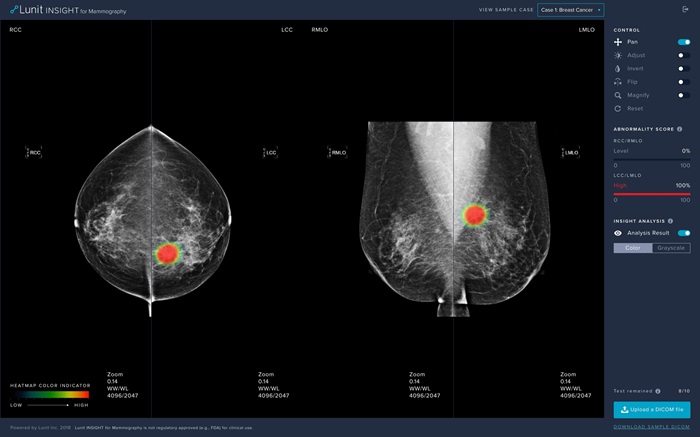
- AI Algorithm Detects 30% Of Breast Cancers Missed on MRI Scans
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered Software Significantly Enhances Brain MRI
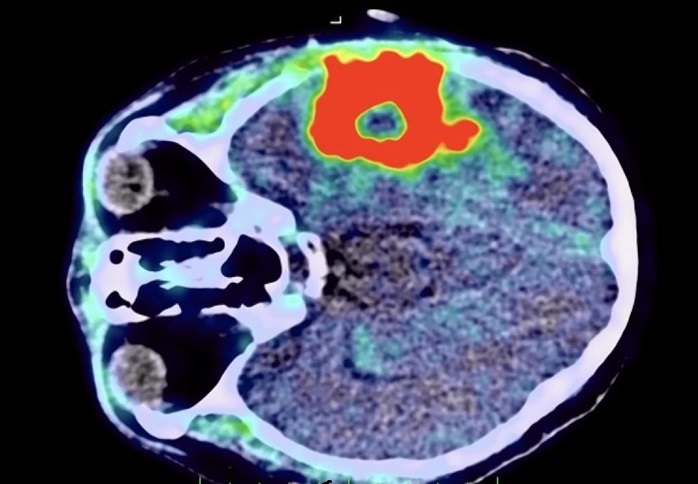
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
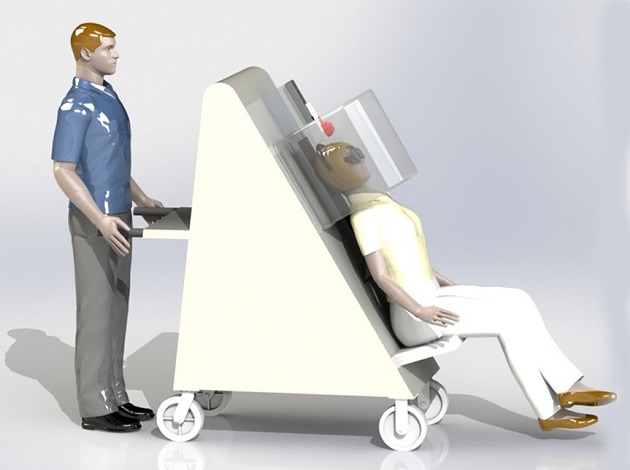
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
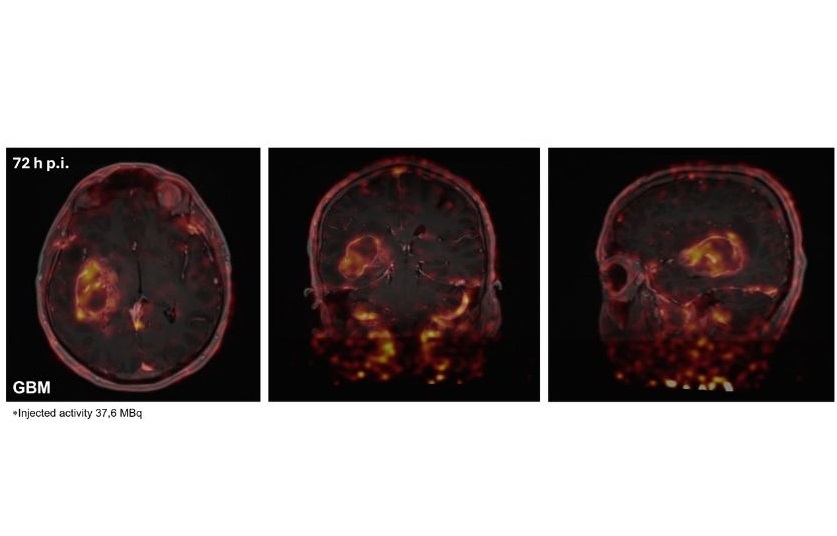
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
- PET Software Enhances Diagnosis and Monitoring of Alzheimer's Disease
- New Photon-Counting CT Technique Diagnoses Osteoarthritis Before Symptoms Develop
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
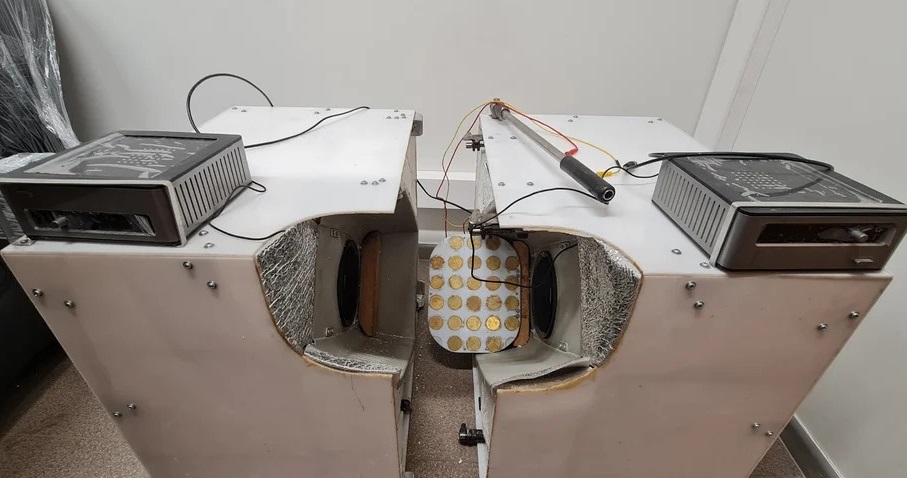
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
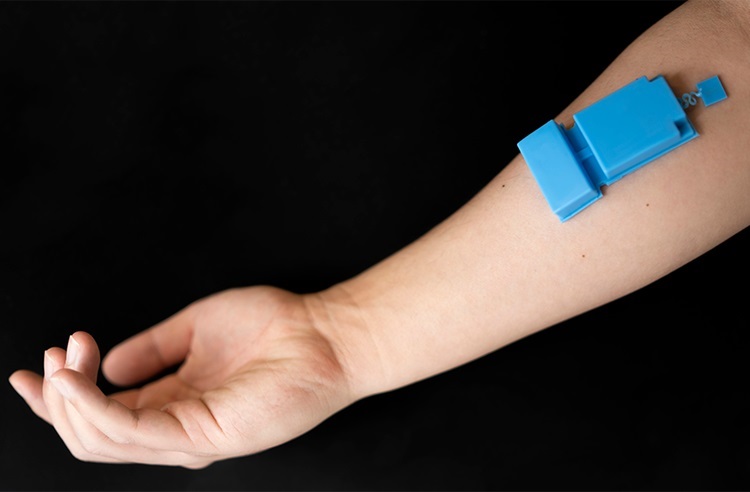
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring
- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment
- New Guideline on Handling Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Samples
- Automated Multi-Patient CT Injection System Reduces Patient Set-Up Time and Streamlines Workflows
- Low-Dose CT Screening for Lung Cancer Can Benefit Heavy Smokers
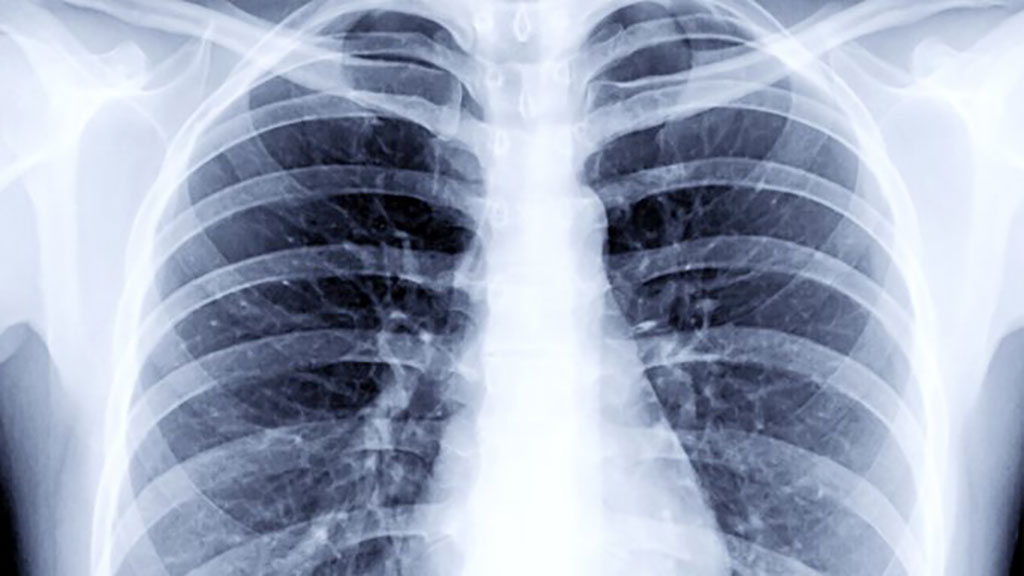
- Non-Invasive Imaging Technique Accurately Detects Aggressive Kidney Cancer
- AI Algorithm Reduces Unnecessary Radiation Exposure in Traumatic Neuroradiological CT Scans
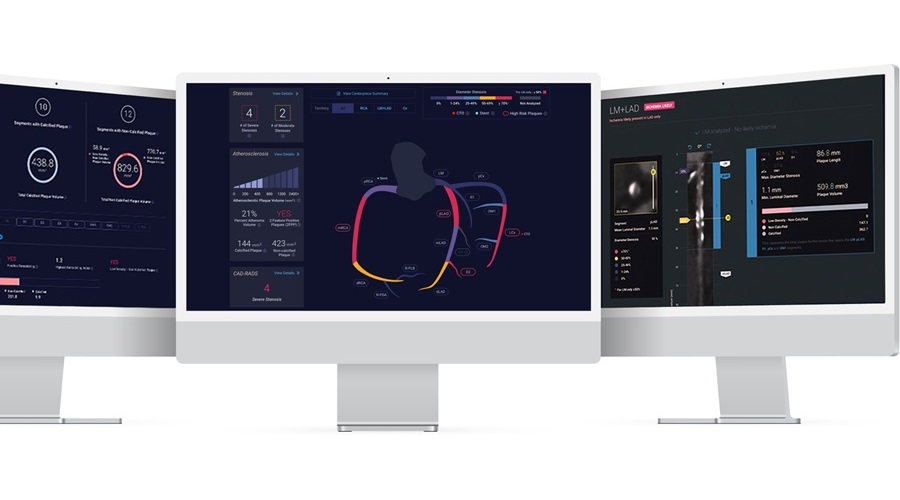
- New Solution Enhances AI-Based Quality Control and Diagnosis in Medical Imaging
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events
Advertise with Us


- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
- AI Model Identifies Vertebral Compression Fractures in Chest Radiographs
- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
- MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy Reduces Long-Term Side Effects in Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Imaging Techniques Could Enable Surgical Removal of Prostate Cancer Without Biopsy
- AI Supported Detection of Cerebral Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Cuts Radiologic Reporting Times
- AI Algorithm Detects 30% Of Breast Cancers Missed on MRI Scans
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered Software Significantly Enhances Brain MRI
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
- PET Software Enhances Diagnosis and Monitoring of Alzheimer's Disease
- New Photon-Counting CT Technique Diagnoses Osteoarthritis Before Symptoms Develop
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring
- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment
- New Guideline on Handling Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Samples
- Automated Multi-Patient CT Injection System Reduces Patient Set-Up Time and Streamlines Workflows
- Low-Dose CT Screening for Lung Cancer Can Benefit Heavy Smokers
- Non-Invasive Imaging Technique Accurately Detects Aggressive Kidney Cancer
- AI Algorithm Reduces Unnecessary Radiation Exposure in Traumatic Neuroradiological CT Scans
- New Solution Enhances AI-Based Quality Control and Diagnosis in Medical Imaging
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer


















 (1).jpg)

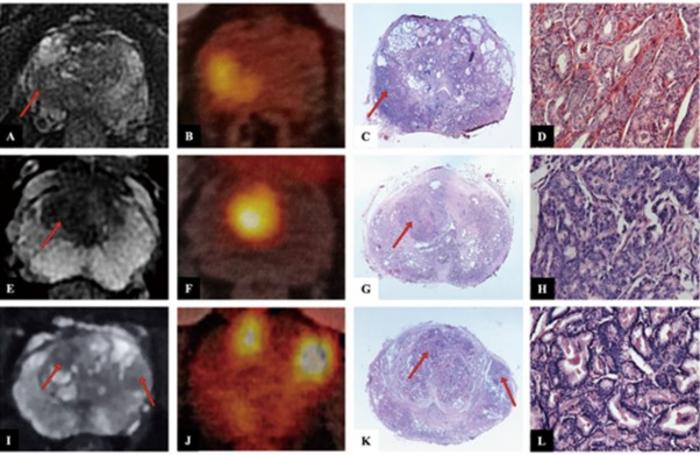


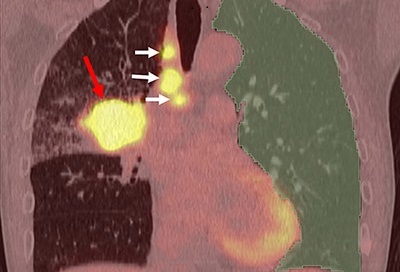

![Image: A kidney showing positive [89Zr]Zr-girentuximab PET and histologically confirmed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Dr. Brian Shuch/UCLA Health) Image: A kidney showing positive [89Zr]Zr-girentuximab PET and histologically confirmed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Dr. Brian Shuch/UCLA Health)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-10-04/ca9scan.jpg)