Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Radiography
UltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- Portable MRI Shows Promise for Expanding Brain Imaging for Alzheimer’s Disease
- MRI-Based Imaging Technique Enables Rapid Assessment of Ovarian Cancer Subtypes and Treatment Response
- Enhanced Cardiovascular MRI Predicts Heart Risk in Children with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- 10-Minute Brain Scan Predicts Effectiveness of Spinal Cord Surgery
- New Compounds to Benefit Kidney Disease Patients Unable to Undergo MRI Examinations
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring
- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
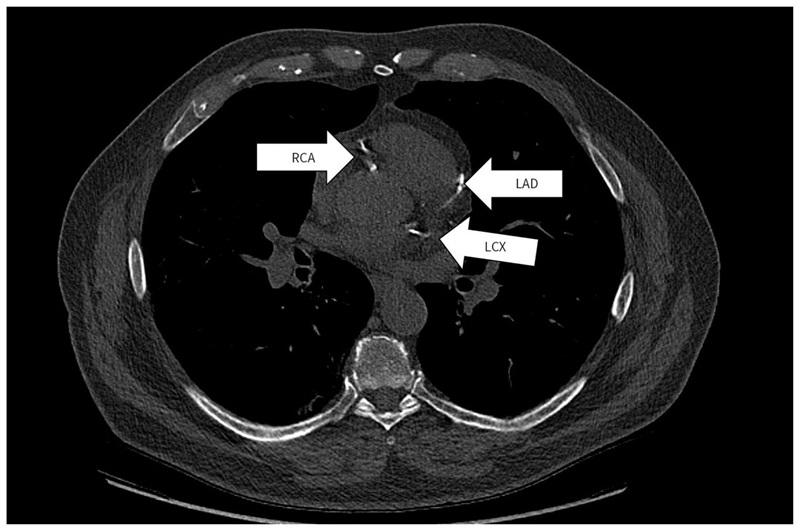
- AI Tool Offers Opportunistic Screening for Heart Disease Using Repurposed CT Scans
- Lung Scans Detect Heart Disease in Patients Without Cardiac Symptoms
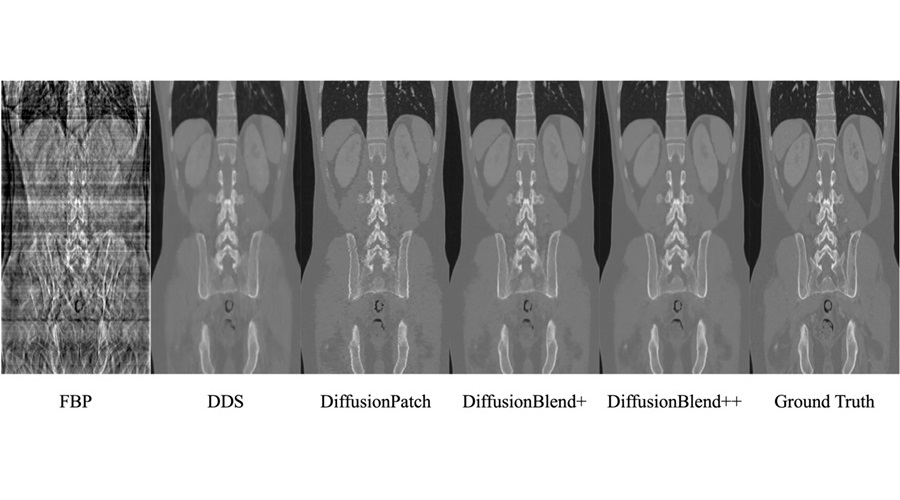
- AI Algorithms Accurately Predict Tumor Location and Size from Medical Images
- AI-Enabled Plaque Assessments Help Cardiologists Identify High-Risk CAD Patients
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Radiography
UltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Radiography
UltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- Portable MRI Shows Promise for Expanding Brain Imaging for Alzheimer’s Disease
- MRI-Based Imaging Technique Enables Rapid Assessment of Ovarian Cancer Subtypes and Treatment Response
- Enhanced Cardiovascular MRI Predicts Heart Risk in Children with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- 10-Minute Brain Scan Predicts Effectiveness of Spinal Cord Surgery
- New Compounds to Benefit Kidney Disease Patients Unable to Undergo MRI Examinations
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring
- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
- AI Tool Offers Opportunistic Screening for Heart Disease Using Repurposed CT Scans
- Lung Scans Detect Heart Disease in Patients Without Cardiac Symptoms
- AI Algorithms Accurately Predict Tumor Location and Size from Medical Images
- AI-Enabled Plaque Assessments Help Cardiologists Identify High-Risk CAD Patients
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer


















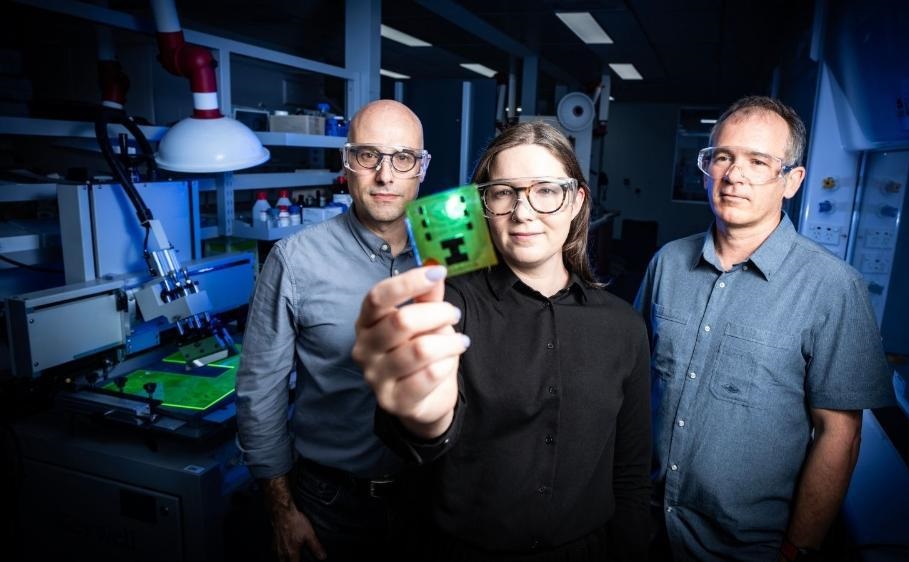
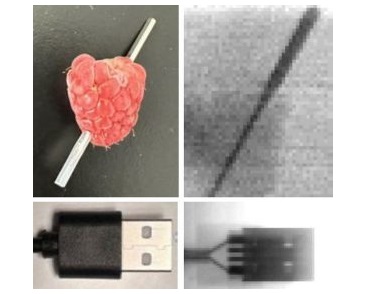
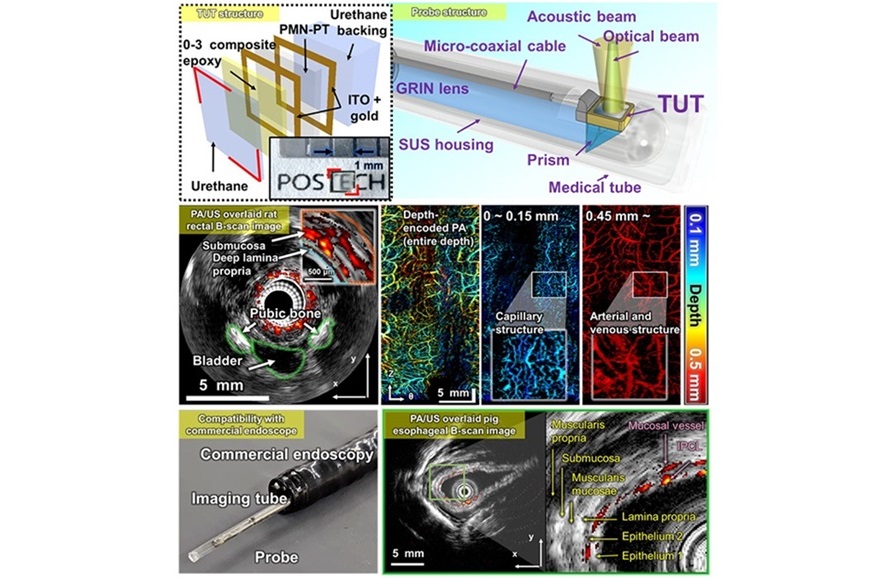

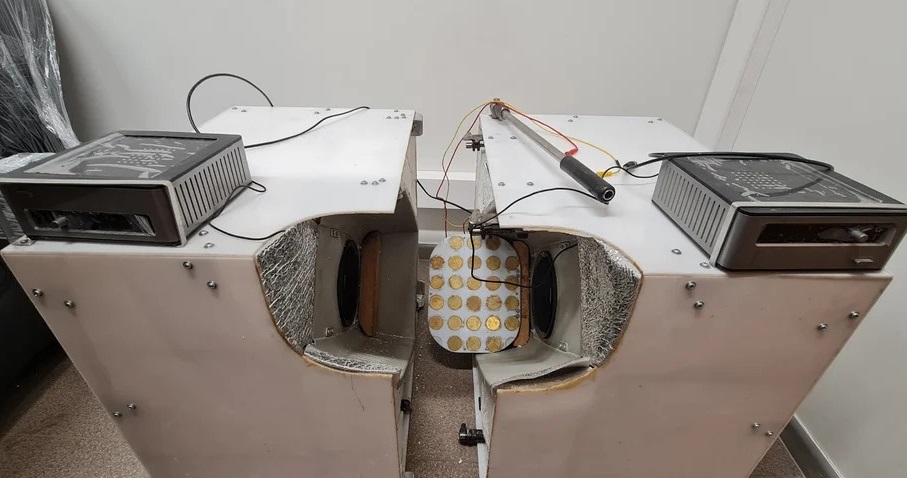
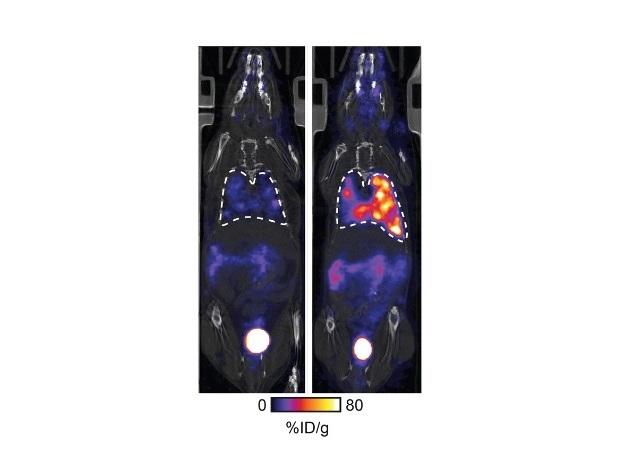

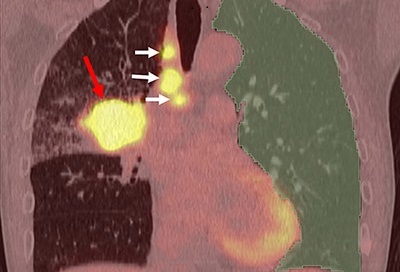
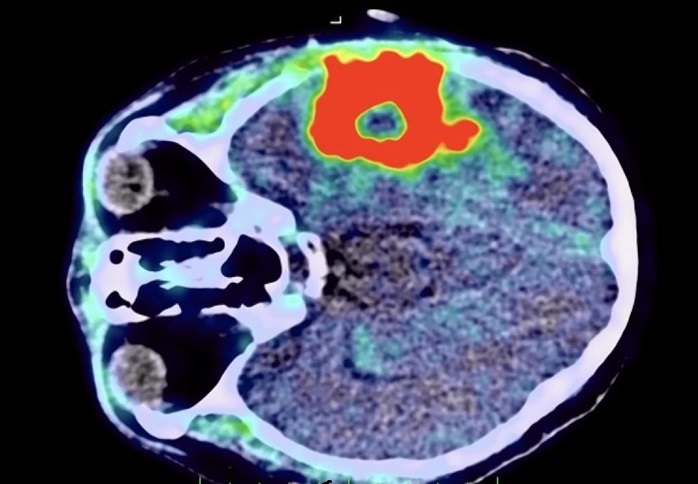





.jpg)
.jpeg)