Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
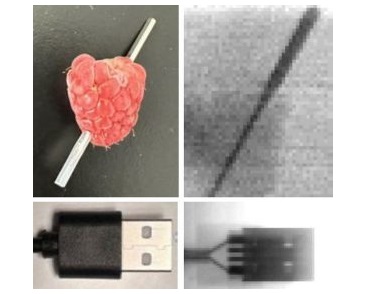
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
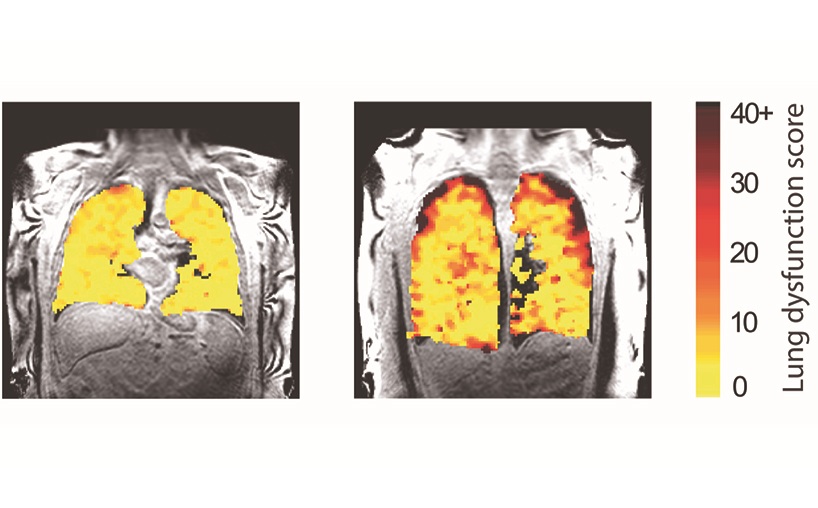
- New Scan Method Shows Effects of Treatment on Lung Function in Real Time
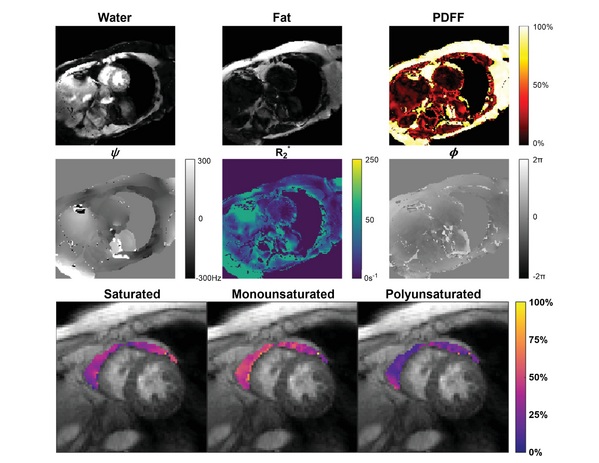
- Simple Scan Could Identify Patients at Risk for Serious Heart Problems
- Pioneering MRI Technique Detects Pre-Malignant Pancreatic Lesions for The First Time
- Portable MRI Shows Promise for Expanding Brain Imaging for Alzheimer’s Disease
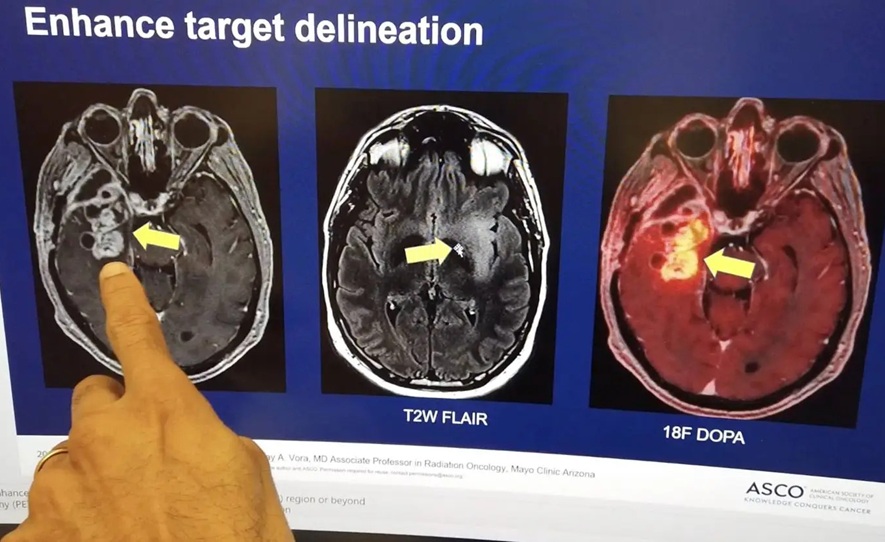
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
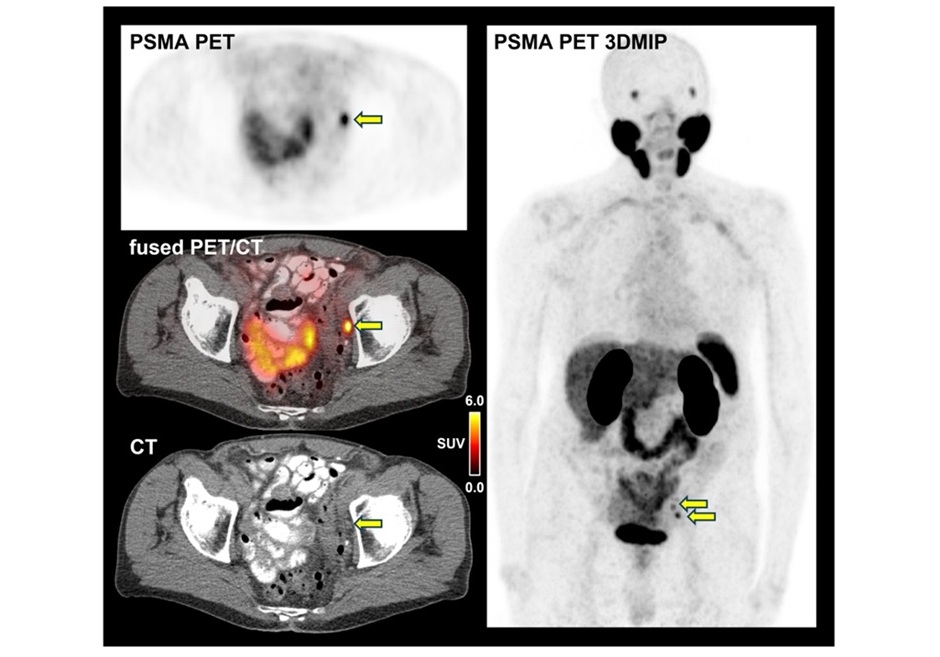
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
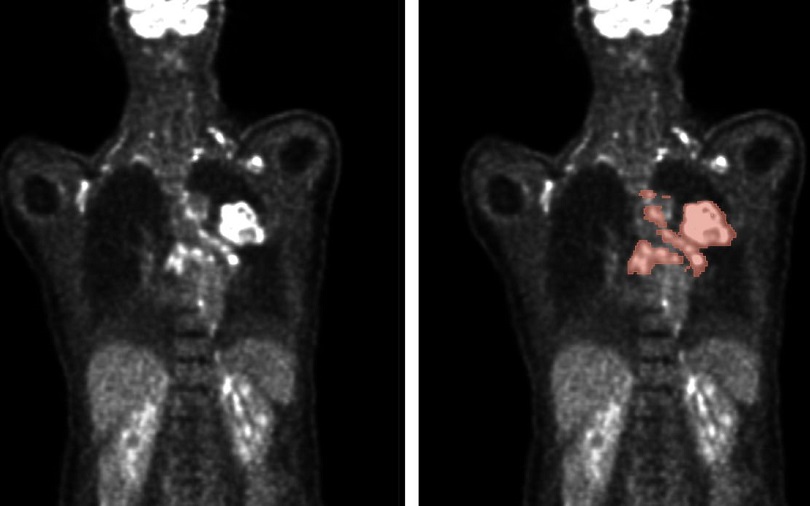
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
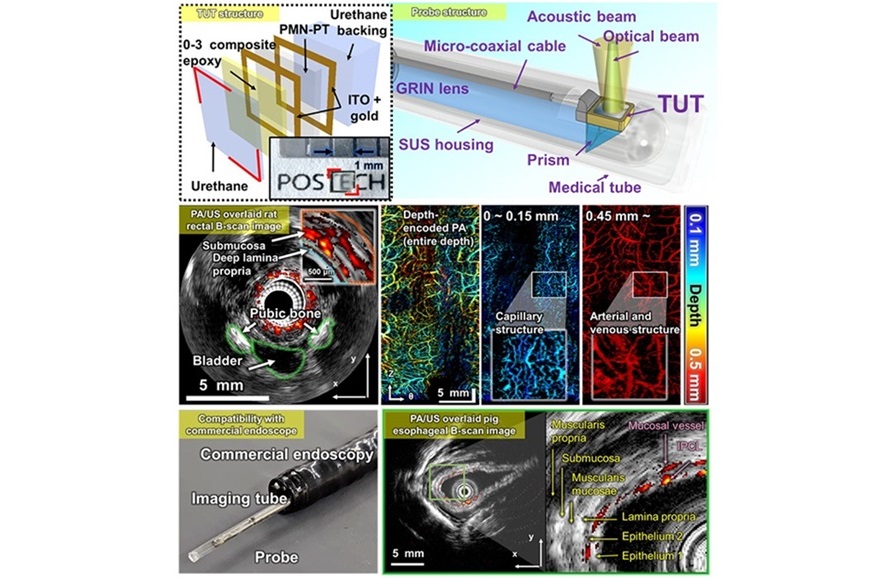
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
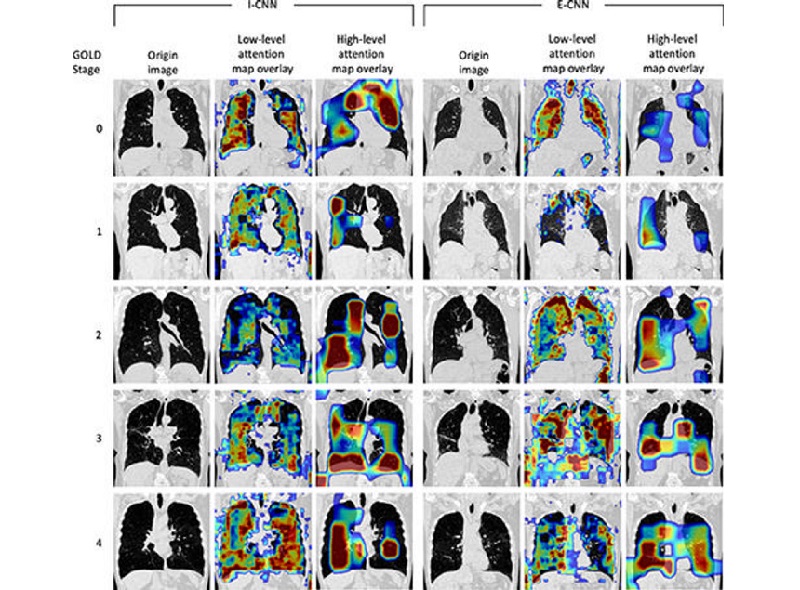
- Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD Using Single Inhalation Lung CT Scan
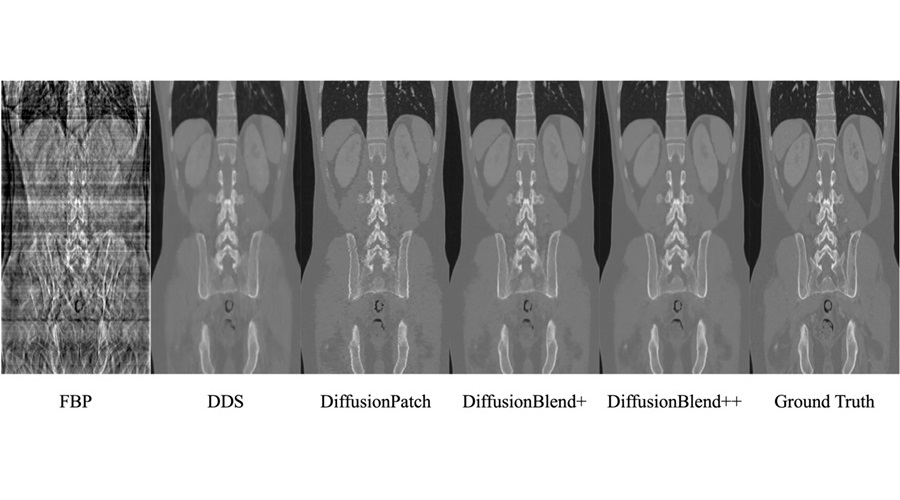
- AI Model Reconstructs Sparse-View 3D CT Scan With Much Lower X-Ray Dose
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
- AI Tool Offers Opportunistic Screening for Heart Disease Using Repurposed CT Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
- New Scan Method Shows Effects of Treatment on Lung Function in Real Time
- Simple Scan Could Identify Patients at Risk for Serious Heart Problems
- Pioneering MRI Technique Detects Pre-Malignant Pancreatic Lesions for The First Time
- Portable MRI Shows Promise for Expanding Brain Imaging for Alzheimer’s Disease
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
- Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD Using Single Inhalation Lung CT Scan
- AI Model Reconstructs Sparse-View 3D CT Scan With Much Lower X-Ray Dose
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
- AI Tool Offers Opportunistic Screening for Heart Disease Using Repurposed CT Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer

















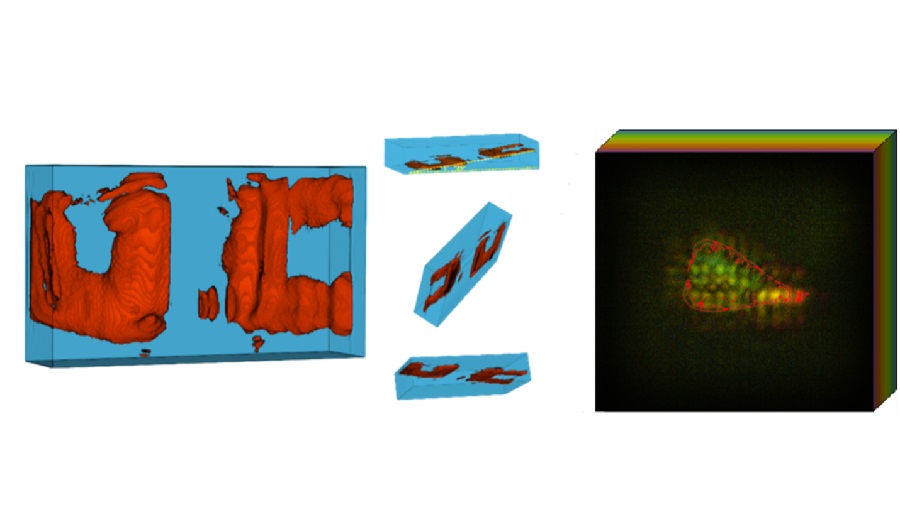


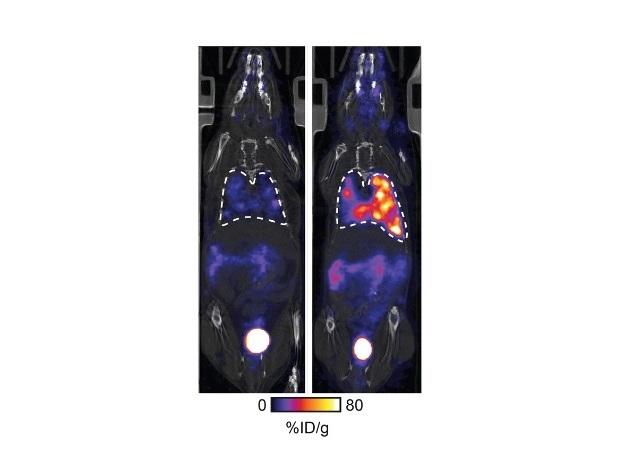
![Image: [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT imaging of patient with primary lung cancer (Photo courtesy of Jiao Tong University) Image: [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT imaging of patient with primary lung cancer (Photo courtesy of Jiao Tong University)](https://globetechcdn.com/medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-12-26/WeiFig6_2.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpeg)